在hadoop体系中,HDFS是最基础也是最核心的部分,本次hadoop源码阅读,首先会从HDFS开始,逐一从各个组件开始分析,然后细化到各个单独的features。
NameNode部分,主要从以下几个方面开始:
- NameNode 结构和功能
- NameNode启动和关闭流程
- NameNode如何管理Slave
- NameNode 重要组件
- NameNode HA机制
- ……待续
1.NameNode
NameNode作为hdfs的master节点,负责管理整个集群元数据和集群管理功能。NameNode代码在org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode包下。
由于NN是通过master/slave方式管理整个集群,它的主要功能如下:
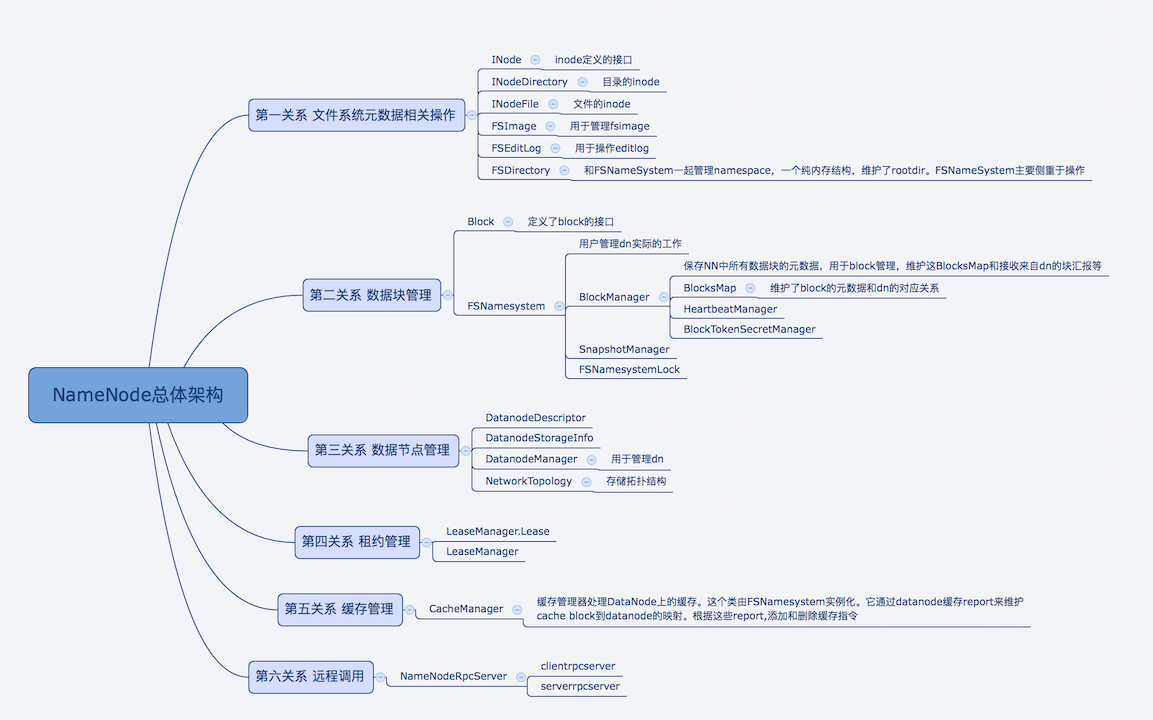
1.文件系统元数据操作
通过FSDirectory管理整个文件系统元数据的目录树
2.数据块的管理
保存NN中所有数据块的元数据,用于block管理,维护这BlocksMap和接收来自dn的块汇报等
3.数据节点管理
namenode用于管理datanode,包含了decommission和activities的节点,用于接收dn注册,心跳等
4.租约管理
用于管理文件访问的租约
5.缓存管理
缓存管理器处理DataNode上的缓存。这个类由FSNamesystem实例化。它通过datanode缓存report来维护cache block到datanode的映射。根据这些report,添加和删除缓存指令
6.提供客户端和slave远程方法调用
创建了ServerRPCServer和ClientRPCServer用于处理客户端和slave请求
重点说明一下NameNode中比较重要的数据结构:
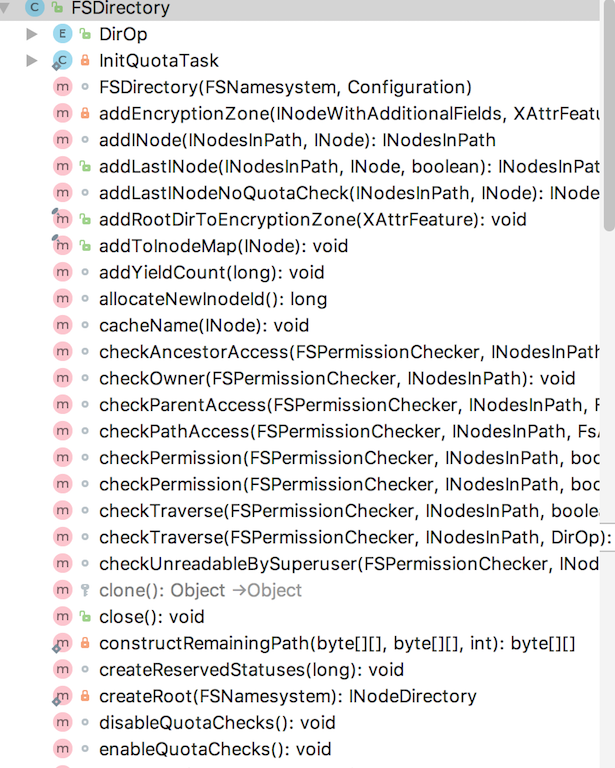
FSDirectory
INodeDirectory rootDir;//用于记录目录树的根路径
private final FSNamesystem namesystem; //FSNameSystem对象
private volatile boolean skipQuotaCheck = false; //skip while consuming edits 是否跳过quota检测
private final int maxComponentLength; //目录中每个Component的最大长度
private final int maxDirItems; //目录里最大的文件数量
private final INodeMap inodeMap; // Synchronized by dirLock 存储了inodeid和Inode的对应关系
private int quotaInitThreads; //用于在启动NN后,初始化quota的线程数量
private final FSEditLog editLog; //FSEditlog对象,用于写editlog
主要方法有:
我们详细看一下在我们调用FileSystem.create之后,在FSDirectory是如何添加文件的:
在指定的Inode
@VisibleForTesting
public INodesInPath addLastINode(INodesInPath existing, INode inode,
boolean checkQuota) throws QuotaExceededException {//在一个存在的目录下边创建文件
assert existing.getLastINode() != null &&
existing.getLastINode().isDirectory();
final int pos = existing.length();//查看路径level
// Disallow creation of /.reserved. This may be created when loading
// editlog/fsimage during upgrade since /.reserved was a valid name in older
// release. This may also be called when a user tries to create a file
// or directory /.reserved.
if (pos == 1 && existing.getINode(0) == rootDir && isReservedName(inode)) {
throw new HadoopIllegalArgumentException(
"File name \"" + inode.getLocalName() + "\" is reserved and cannot "
+ "be created. If this is during upgrade change the name of the "
+ "existing file or directory to another name before upgrading "
+ "to the new release.");
}
//获取创建目录的上一级InodeD
final INodeDirectory parent = existing.getINode(pos - 1).asDirectory();
// The filesystem limits are not really quotas, so this check may appear
// odd. It's because a rename operation deletes the src, tries to add
// to the dest, if that fails, re-adds the src from whence it came.
// The rename code disables the quota when it's restoring to the
// original location because a quota violation would cause the the item
// to go "poof". The fs limits must be bypassed for the same reason.
if (checkQuota) {//是否检测quota
final String parentPath = existing.getPath();
verifyMaxComponentLength(inode.getLocalNameBytes(), parentPath);
verifyMaxDirItems(parent, parentPath);
}
// always verify inode name 验证inode name
verifyINodeName(inode.getLocalNameBytes());
//通过块存储策略来计算quota使用量
final QuotaCounts counts = inode.computeQuotaUsage(getBlockStoragePolicySuite());
//更新父目录的quota
updateCount(existing, pos, counts, checkQuota);
boolean isRename = (inode.getParent() != null);
boolean added;
try {
added = parent.addChild(inode, true, existing.getLatestSnapshotId());
} catch (QuotaExceededException e) {
updateCountNoQuotaCheck(existing, pos, counts.negation());
throw e;
}
if (!added) {
updateCountNoQuotaCheck(existing, pos, counts.negation());
return null;
} else {
if (!isRename) {
AclStorage.copyINodeDefaultAcl(inode);
}
addToInodeMap(inode);
}
//quota更新成功后,在对应父目录的InodePath中添加此inode对象
return INodesInPath.append(existing, inode, inode.getLocalNameBytes());
}
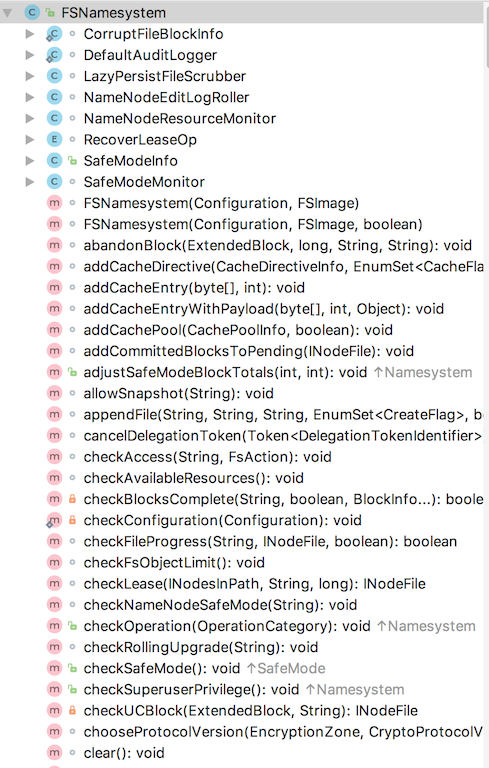
FSNamesystem
FSNamesystem 是NN中最重要的类,实际记录了dn上所有的工作状态。
重要的参数有
FSDirectory dir; FSDirectory
private final BlockManager blockManager; //保存NN中所有数据块的元数据,用于block管理,维护这BlocksMap和接收来自dn的块汇报等
private final SnapshotManager snapshotManager; //用于Snapshot的管理
private final CacheManager cacheManager; //用于管理dn上的Cache
private final DatanodeStatistics datanodeStatistics; //用于记录dn的统计信息,例如心跳汇报等
此类的方法很多,主要用于管理dn上报的比如心跳汇报,块汇报等,用于管理集群slave和数据块。
我们重点看一下FSNameSystem是如何处理dn发送过来的心跳汇报的
//用于记录dn发送过来的心跳,确保dn不心跳超时,同时发送command给dn
HeartbeatResponse handleHeartbeat(DatanodeRegistration nodeReg,
StorageReport[] reports, long cacheCapacity, long cacheUsed,
int xceiverCount, int xmitsInProgress, int failedVolumes,
VolumeFailureSummary volumeFailureSummary,
boolean requestFullBlockReportLease) throws IOException {
readLock();
try {
//get datanode commands
final int maxTransfer = blockManager.getMaxReplicationStreams()
- xmitsInProgress;
//nn通过调用DataNodeManager的handleHeartbeat方法进行心跳汇报的处理,生成一组需要被dn执行的cmds命令
DatanodeCommand[] cmds = blockManager.getDatanodeManager().handleHeartbeat(
nodeReg, reports, blockPoolId, cacheCapacity, cacheUsed,
xceiverCount, maxTransfer, failedVolumes, volumeFailureSummary);
long blockReportLeaseId = 0;
if (requestFullBlockReportLease) {
blockReportLeaseId = blockManager.requestBlockReportLeaseId(nodeReg);
}
//create ha status 获取当前NS的HA状态
final NNHAStatusHeartbeat haState = new NNHAStatusHeartbeat(
haContext.getState().getServiceState(),
getFSImage().getCorrectLastAppliedOrWrittenTxId());
//生成HeartbeatResponse返回给dn
return new HeartbeatResponse(cmds, haState, rollingUpgradeInfo,
blockReportLeaseId);
} finally {
readUnlock("handleHeartbeat");
}
}
